If you’re planning to install a rooftop solar system, you’ve likely come across three main types: on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid systems. Each serves a different purpose and suits different needs.
In this blog, we’ll explain in simple language the differences between these solar systems, how they work, their pros and cons, and which one is right for your home or business.

What Are the 3 Types of Solar Systems?
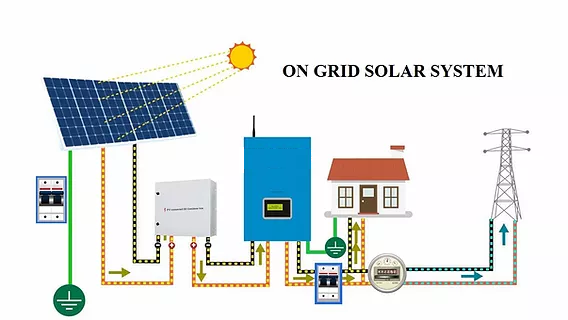
On-Grid Solar System (Grid-Tied)
This system is connected to the government electricity grid. It does not use batteries.
How it works:
- Solar panels generate electricity.
- You use the electricity during the day.
- Extra power is sent to the grid.
- If needed, you can draw power from the grid at night or during cloudy days.
Best for:
Homes and businesses in cities with stable power supply.
Advantages:
- Lower cost (no batteries)
- Eligible for net metering
- Government subsidy applicable
Disadvantages:
- No power backup during power cuts
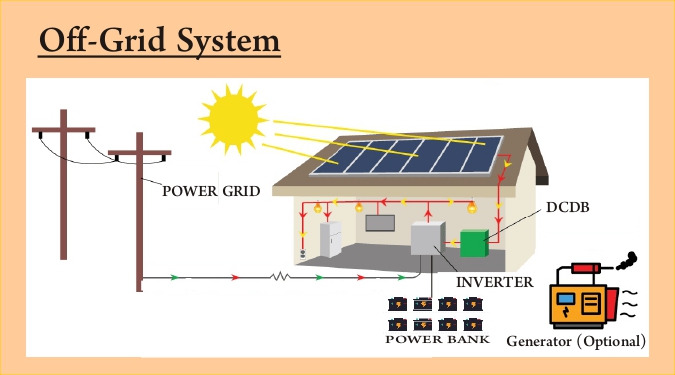
Off-Grid Solar System (Stand-Alone)
This system works independently of the electricity grid. It uses batteries to store solar power.
How it works:
- Panels generate electricity → stored in batteries.
- You use stored power during night or when panels aren’t producing.
Best for:
Remote areas, villages, farms where grid electricity is unreliable or unavailable.
Advantages:
- Works during power cuts
- Complete independence from electricity bills
Disadvantages:
- High upfront cost
- Batteries need maintenance and replacement every 5–7 years
- No subsidy in most states
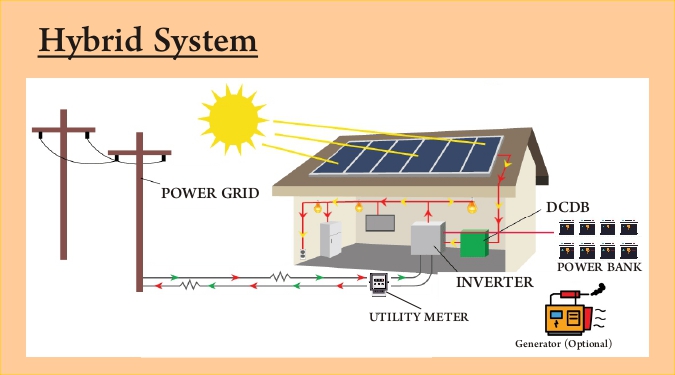
Hybrid Solar System
This is a combination of on-grid and off-grid systems. It uses both the grid and batteries.
How it works:
- Uses solar power first.
- Stores excess energy in batteries.
- Sends extra to the grid.
- Uses grid power only if solar + battery are exhausted.
Best for:
Homes and businesses that need backup power but also want to enjoy net metering benefits.
Advantages:
- Works during power cuts
- Can export power to the grid
- Energy security + savings
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost due to batteries and inverter
- Slightly more complex setup
Comparison Table: On-Grid vs Off-Grid vs Hybrid
| Feature | On-Grid | Off-Grid | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Required | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Works During Power Cut | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Net Metering | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Government Subsidy | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (for on-grid part) |
| Ideal For | Cities, towns | Remote areas | Cities needing backup |
| Cost (₹) | Lowest | Highest | Moderate–High |
Which System Is Right for You?
| Scenario | Recommended System |
|---|---|
| Live in a city with no power cuts | On-Grid |
| Live in a village or farm | Off-Grid |
| Want savings + backup during power cuts | Hybrid |
| Want lowest initial cost | On-Grid |
| Need 24/7 power for business or medical use | Hybrid or Off-Grid |
Cost Comparison (2025)
| System Type | Average Cost for 5kW (₹) | Maintenance | Payback Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Grid | ₹2.2 – ₹2.5 lakh | Low | 4–5 years |
| Off-Grid | ₹4 – ₹4.5 lakh | Medium | 6–8 years |
| Hybrid | ₹4.5 – ₹5.5 lakh | Medium | 5–6 years |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I switch from on-grid to hybrid later?
Yes. You can upgrade your on-grid system to hybrid by adding compatible inverter and battery storage.
2. Can I install an off-grid system in the city?
Yes, but it won’t be eligible for subsidy and you won’t get net metering benefits.
3. Is hybrid better than on-grid?
Hybrid gives backup during power cuts, but costs more. If you have stable power and want faster ROI, on-grid is better.
4. How long do solar batteries last?
Most batteries last 5–7 years. Lithium-ion batteries may last longer (8–10 years) but cost more.
5. Can I get subsidy for hybrid system?
Yes, but only the on-grid portion is covered. Battery costs are usually not subsidized.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solar system depends on your location, electricity needs, budget, and whether you face power cuts. Here’s a simple takeaway:
- On-grid: Maximum savings + subsidy, no backup
- Off-grid: Full independence + backup, but costly
- Hybrid: Best of both, but higher upfront investment
Consult a trusted solar provider to assess your site, calculate savings, and choose the best system.

